In the realm of healthcare, a world where every word carries a life-altering weight, communication stands as the bridge between hope and healing. However, for medical professionals with accents, language barriers can pose challenges that need to be addressed proactively.
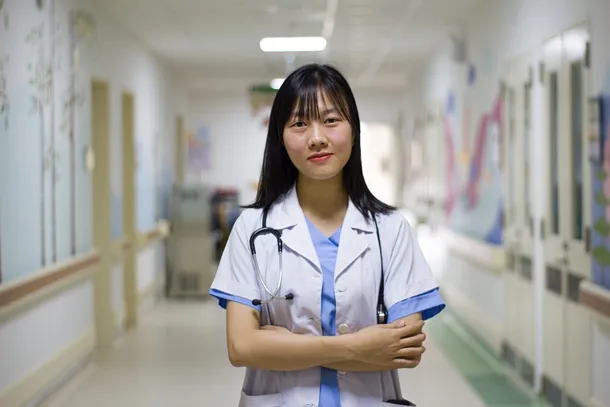
Consider the story of Dr. Alvarez, a skilled physician from Guatemala practicing in the heart of New York City. Dr. Alvarez's commitment to her patients was undeniable, but she faced a challenge that echoed in the bustling corridors of the hospital—a subtle language barrier due to her Guatemalan accent.
One day, a simple mispronunciation led to a minor misunderstanding with a patient, causing brief confusion. Dr. Alvarez realized that clear communication was not just essential; it was a lifeline in healthcare. Her journey to improve her communication skills is a testament to the critical role that effective communication plays in providing quality care.
In this article, we explore strategies for medical professionals like Dr. Alvarez, who are dedicated to ensuring that their patients always feel heard and understood.
The Importance of Clear English in Healthcare Clear communication is the cornerstone of safe and effective healthcare delivery. Inaccurate or misunderstood information can lead to misdiagnoses, incorrect treatment plans, and even patient harm. The consequences of miscommunication in healthcare are far-reaching and can have serious implications for both patients and healthcare providers.
Medical professionals with accents often face unique challenges in their day-to-day work. Patients may have difficulty understanding them, leading to frustration and potential misinterpretations. Additionally, accents can sometimes lead to biases or stereotypes, which can affect patient-provider relationships. It's essential to acknowledge these challenges and work towards effective solutions.
Overcoming English Pronunciation and Accent Challenges Effective communication in healthcare hinges on clear and precise pronunciation, specifically one that native English speakers can easily recognize. If you work in the United States, the general American accent will often use different pronunciations of words that may share the same spelling in your native language. So, for medical professionals who have accents in English, addressing pronunciation challenges and learning the American accent is pivotal.
Here are practical strategies and some examples of tricky words and phrases in medical contexts:
1. Focus on Problematic Medical Terminology
Example: "Sphygmomanometer"
Medical jargon is rife with complex terms, such as "sphygmomanometer" (blood pressure cuff). Dedicate time to mastering these words through repeated practice, ensuring that patients can understand critical information without confusion.
2. Tackle Tricky Consonants like TH
Example: "Thrombosis"
Certain consonants like "th" can be very tricky for non-native English speakers, as that sound doesn't exist in many languages. Practice enunciating words like "thyroid" and "thrombosis" clearly to avoid misunderstandings during diagnosis discussions.
3. Articulate Drug Names Accurately
Example: "Ibuprofen"
Precision in drug pronunciation is vital. Accurate articulation of medication names like "ibuprofen" ensures patients take the right treatment and dosage. Spelling in English is very unhelpful when it comes to pronunciation, so be sure to double-check the pronunciation of drug names and not assume by relying on spelling.
4. Work on Pronunciation of Patient Instructions
Example: "Take with Food"
Clear instructions are essential. Pronounce patient guidance like "take with food" distinctly to prevent medication errors. In words like "food", ensure a clear pronunciation of the vowel sound. Clear vowel pronunciation is typically the first part of mastering the American Accent.
5. Enhance Speech Clarity in Emergency Scenarios
Example: "Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)"
During critical situations, every second counts. Focus on clarity when pronouncing emergency terms like "CPR", clearly enunciating every sound, and stressing the last "R" sound in the acronym, to ensure an effective response.
6. Practice Complex Disease Names
Example: "Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)"
Complex disease names can be tongue twisters. Regular practice of terms like "GERD" aids in patient comprehension and informed decision-making.
7. Embrace Multisyllabic Words
Example: "Hemorrhage"
Multisyllabic words are common in medical contexts. Developing fluency in pronunciation, as with "hemorrhage," ensures effective communication. Working on placing the word stress in the right syllable is critical to avoid misunderstandings. American English speakers spend more time on the stressed syllable, so work on finding the stressed syllable of each word and ensure that you elongate it in comparison to the rest of the word.
8. Record and Self-Assess Patient Interactions
Example: Playback of Consultations
Recording and reviewing patient interactions provide opportunities for self-assessment. Listen to consultations to identify areas for improvement, such as specific words that you struggle with that lead to patient misunderstanding. You can then listen to these word pronunciations in an online dictionary, and even better, practice your pronunciation of these words on the BoldVoice app and get instant feedback on your pronunciation accuracy.
Developing Effective Listening Skills Patients rely on medical professionals to understand their concerns, symptoms, and needs. Here are strategies and examples to help medical professionals enhance their listening skills. These also generally apply to native-English-speaking healthcare professionals, but can be particularly helpful for immigrant healthcare professionals in the US and Canada due to potential cultural differences.
1. Maintain Unwavering Focus
Example: Patient Describing Symptoms
During patient consultations, maintain unwavering eye contact and provide undivided attention. Patients should feel heard and valued when discussing their health concerns.
2. Active Listening and Empathy
Example: Acknowledging Emotional Distress
Active listening involves not only hearing but also empathizing with the patient's emotions. When a patient expresses anxiety or sadness, acknowledge their feelings to create a supportive environment.
3. Ask Clarifying Questions
Example: Patient's Medication Regimen
To ensure complete understanding, ask clarifying questions. For instance, when discussing a complex medication regimen, inquire if the patient is clear about the dosage and timing.
4. Avoid Rushing or Interrupting
Example: Patient Describing Symptoms
In the rush of a busy healthcare environment, avoid rushing through patient interactions. Allow patients to express themselves fully without interruption, which can lead to incomplete information.
5. Use Reflective Listening
Example: Patient Sharing Concerns
Reflective listening involves paraphrasing what the patient has said to confirm understanding. For instance, if a patient expresses concerns about a treatment's side effects, respond with, "I understand you're worried about potential side effects."
6. Non-Verbal Communication
Example: Patient's Discomfort
Non-verbal cues such as body language can reveal patients' discomfort or anxiety. Pay attention to these cues and respond accordingly, offering reassurance or addressing concerns.
7. Mindful Note-Taking
Example: Documenting Patient History
When taking notes, do so mindfully without detracting from the conversation. Accurate documentation of patient history and concerns is essential for comprehensive care.
8. Provide Encouragement for Questions
Example: Patient Seeking Clarification
Encourage patients to ask questions and seek clarification. Patients who actively participate in their care can make informed decisions.
9. Handling Emotional Disclosure
Example: Patient Sharing Personal Information
Sometimes, patients may share sensitive or emotional information. Maintain a supportive and non-judgmental attitude, fostering trust.
Cultural Competence and Sensitivity Cultural competence is a vital aspect of effective communication in healthcare. By understanding and respecting patients' cultural backgrounds, medical professionals can create a more inclusive and supportive environment. Key considerations include:
1. Learning American Cultural Norms and Practices
As a non-American healthcare professional in the US, it's essential to familiarize yourself with American cultural norms and practices. For instance, Americans often value individual autonomy in healthcare decision-making and appreciate direct and transparent communication.
2. Adapting Communication Styles to American Preferences
Adapting your communication style to align with American preferences is vital. Americans generally appreciate a friendly and informal approach. Address patients by their preferred titles, use clear and straightforward language, and engage in active listening.
3. Avoiding Assumptions and Stereotypes
As a non-American healthcare professional, avoid making assumptions or relying on stereotypes about American patients based on their cultural backgrounds. Each patient is unique, and assumptions can lead to misunderstandings.
4. American Patient's Specific Cultural Needs
While English is the predominant language in the US, some patients may have limited English proficiency. Providing interpretation services or translated materials ensures that patients fully comprehend their medical conditions and treatment options.
Also, many Americans hold strong religious beliefs that can impact their healthcare decisions. Understanding and respecting these beliefs, such as the refusal of certain medical procedures for religious reasons, is crucial.
Non-American healthcare professionals should also be aware of healthcare disparities that affect specific racial or ethnic groups in the US. Recognizing these disparities and actively working to reduce them is an important aspect of culturally competent care.
Technology and Communication Tools
Advancements in technology have brought about numerous tools and resources to aid in communication. Consider utilizing:
1. Speech Recognition Software
Speech recognition software allows healthcare professionals to transcribe spoken words into text efficiently. It can be particularly useful for non-native English speakers when taking patient notes or documenting medical information. By reducing the manual transcription workload, it frees up more time for direct patient care.
2. Telehealth Platforms with Interpretation Services
Telehealth platforms have gained prominence, especially in recent times. Many of these platforms offer built-in interpretation services, allowing non-native English-speaking healthcare professionals to provide virtual consultations with American clients seamlessly.
These services bridge language gaps and ensure that patients receive the care they need, regardless of language differences.
3. Tools for Accent Reduction like BoldVoice
BoldVoice is an innovative accent training app designed to help non-native English-speaking professionals improve their pronunciation and communication skills. It offers personalized accent reduction courses and exercises tailored to the specific needs of each user.
By using BoldVoice, healthcare professionals can work on reducing their accents, ensuring clearer and more effective communication with patients. The tool has been designed for very busy professionals like healthcare workers: only 10-15 minutes of practice per day can lead to noticeable improvements in speech clarity and confidence.
The Role of Healthcare Institutions in Communication Training Healthcare institutions and employers play a significant role in supporting medical professionals with accents. They can facilitate training opportunities, promote cultural competence, and foster inclusive environments where every healthcare provider can thrive.
Here are several key ways in which institutions and employers can offer support:
1. Cultural Competence Training
Cultural competence training should be an integral part of healthcare institution curricula. By educating staff about diverse cultures and fostering an understanding of different customs and practices, institutions can create a more inclusive environment that respects the cultural backgrounds of both healthcare providers and patients.
2. Interpreter Services
Employers should ensure that interpreter services are readily available to facilitate communication between healthcare providers and patients with limited English proficiency. This proactive approach ensures that language barriers do not compromise the quality of care.
3. Diversity and Inclusion Initiatives
Institutions and employers can actively promote diversity and inclusion within their healthcare teams. This includes not only hiring a diverse workforce but also creating an environment where all healthcare professionals feel valued, respected, and supported regardless of their cultural or linguistic background.
4. Mentorship and Peer Support
Establishing mentorship programs that pair experienced healthcare professionals with those who are newer to the field can be immensely beneficial. Mentors can offer guidance, share their experiences, and provide emotional support, helping newcomers navigate the challenges they may face, including those related to accents.
5. Flexible Communication Tools
Incorporating technology and communication tools that support healthcare professionals with accents can enhance their ability to provide patient care. For instance, using speech recognition software or telehealth platforms with built-in interpretation services can help bridge language gaps.
6. Accent Reduction Training Programs
Healthcare institutions can provide accent reduction training programs, such as BoldVoice , as part of their professional development initiatives. These programs can help non-native English-speaking medical professionals improve their general American accent. English pronunciation, and overall communication skills, making it easier for them to provide effective patient care.